Mast cells: An amplifier of the inflammatory response
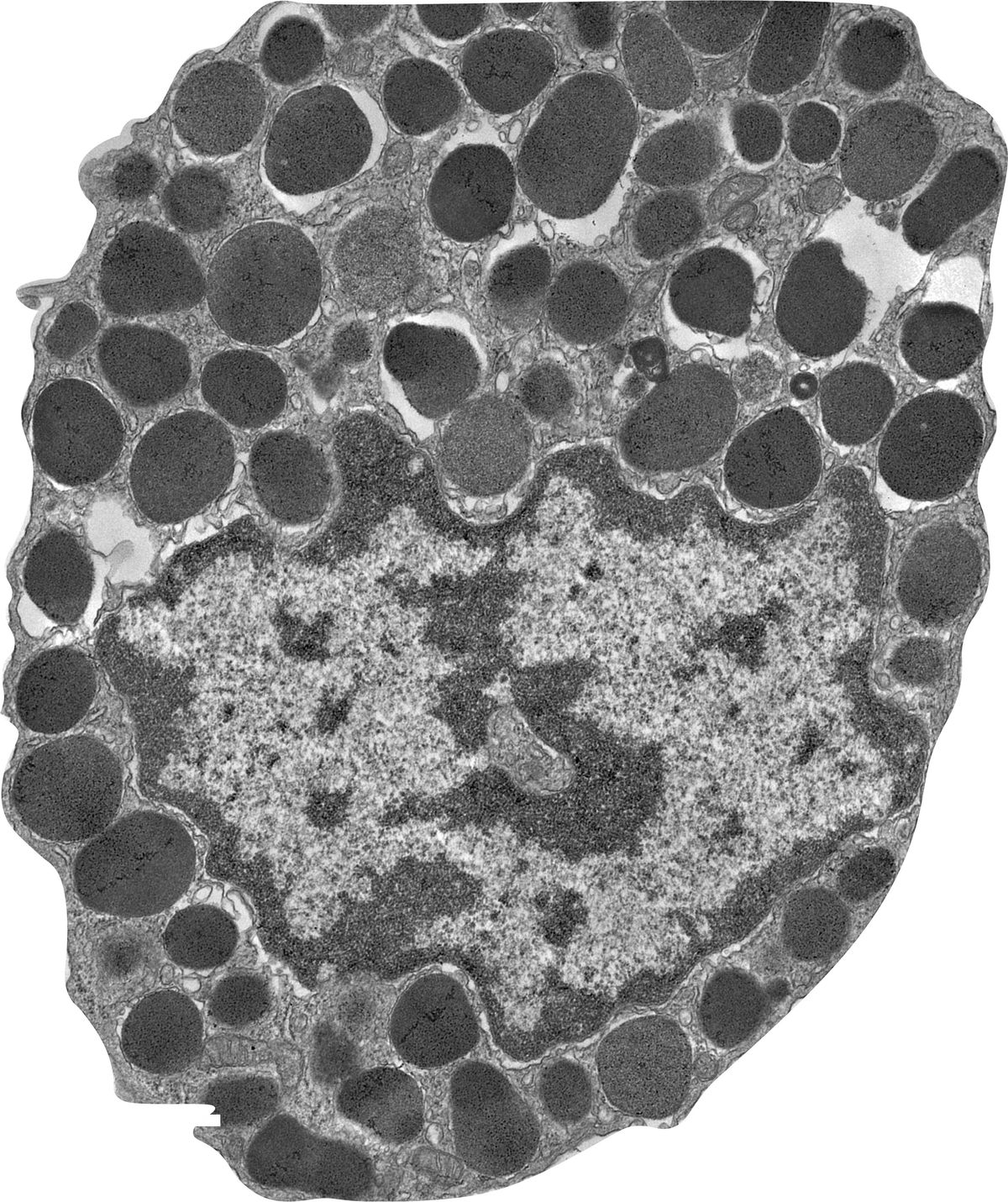
Mast cells are myeloid cells that play an essential role in innate and adaptive immunity. Mast cells recognize harmful antigens by binding to pathogens directly or associating with PAMPs on the mast cell surface. Activated mast cells release inflammatory mediators, including histamine, heparin, a variety of cytokines, chondroitin sulfate, and neutral proteases, which are prepacked in their large granules. These released inflammatory mediators attract leukocytes (eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes, neutrophils) to the inflammatory site and amplify the inflammatory response.
